The best advice from leading database consulting agencies to manage your WordPress website better
WordPress is the king of all CMS platforms right now. That is why you need a database that can keep up with the various features and scalability this CMS platform offers. MySQL database is the favorite of almost all WordPress admins who know a thing or two about database maintenance.
This database uses PHP just like WordPress. Therefore, if you have the knowledge to set up a working site with added functionalities, you should go for a phpMyAdmin package to handle the administration of your website database.
You can perform all frequently used operations including tables, columns, indexes, users, permissions and databases using the phpMyAdmin software. You can enjoy VPS and dedicated server hosting options too. Today, we will help you understand what you need to start using phpMyAdmin –
- First, you will need to set up a domain with full hosting features or mirror hosting on the page. You can manage it by accessing Panel > Domains > Manage Domains. Although, parked, redirect and cloaking options may not function properly at the time.
- If you want to access phpMyAdmin, do not enable Passenger on your host domain. It intercepts the HTTP requests to show an error message.
- You should start by adding a MySQL hostname. Go to Panel > Goodies > MySQL Databases.
- After you add the hostname and the full hosting for the DNS, allow time for your site database to propagate.
After these steps, you can expect to see phpMyAdmin on your site domain.
-
How to locate your database login essentials?
- You can find a listing of your MySQL hostnames and added databases in the Panel > Goodies > MySQL Databases. Using a particular username will tie your new database to the right list. You can find the name on the right of the panel.
- Click on the MySQL username and then click on the Show button to get your password. The user id and password from the MySQL database are your authentication details for logging in to your phpMyAdmin account.
- Insert your username and password in the login page and then click on Go.
This is how you can get your login credentials. To open phpMyAdmin, you can open the URL of your MySQL hostname or click the link to the right.
-
Resetting a password for your WordPress from phpMyAdmin –
What will do if your site is hacked? Before you give a call to your database consulting agency, you need to be able to take steps to secure your website information. This is especially necessary if you are logged out of your site admin panel. You need to know how to reset your password from your phpMyAdmin.
You must already know your existing phpMyAdmin login details. Then, you should also know that you could access your website MySQL database through the cPanel hosting.
Here are a few steps that will help you reset your password –
i. What’s the name of your database?
Your WordPress database has a name. We have already told you how to find out and reset the database name. So go ahead and see the exact location for the password reset.
This is necessary since most of the times you may be running multiple installations with the same database. Start with your wp-config.php file that is located in your root WP Directory.
ii. Locating your database–
Now you should be able to access your MySQL database and browse it via your phpMyAdmin account.
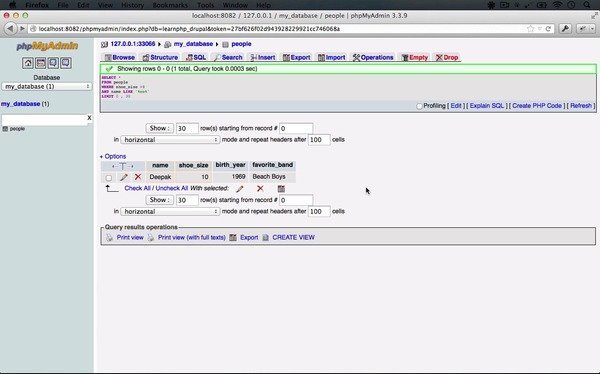
Select the correct database on your left once you are inside the phpMyAdmin dashboard. Look for the name you found from the previous step and click on it. Now you should be able to see a list of the table with a wp_prefix. If you have made any changes to the prefix previously, then you may be looking for something like “wp123_”. Check the list of wp_users and click on it to open it in the browser tab.
iii. How to edit the fields?
To edit the details, you need to click on the “pencil” icon. This will directly take you to the password reset page. You can now edit the user_pass field value here. There will be some “random” characters in the password field. This is because WordPress uses MD5 Hash to store the passwords rather than using plain text options. Therefore, you need to use one of the MD5 Hash generators online to insert the new password. You cannot enter plain text as your site password.
This is the shortest and simplest way to change your WordPress password using phpMyAdmin.
-
How to drop tables from your database?
If you have used your WordPress site for a couple of years now, you may find some available tables. They can cause your database to fragment, and this will slow your site down. Dropping a database refers to the practice of removing a table from a database and removing all its contents too.
Here is one way to do it through phpMyAdmin –
- Select the particular database you want to drop or delete.
- The list of databases on the left column will give you the details you need for your mission.
- Check the tables you want to delete permanently or drop from your website database.
- Go to the dropdown box that says, “With selected” and select “Drop” from the list.
- Double check to make sure that you have selected the right tables for deletion. It will ask you if you want to delete the tables again.
- If your selections are correct, click on yes to drop the table.
This is how you can complete dropping a table from the database including all the details about it.
Managing a WordPress database is no longer a struggle with phpMyAdmin. Managing accounts, login details, and tables is a lot easier once you get to know your way around this software.
Sujain Thomas Author
Sujain Thomas is a senior DBA working with a reputed database consulting agency in the US. Her firm manages some of the biggest e-commerce accounts and business websites in the history of the internet.